

However, lots of people have done lots of work measuring bond strengths, and they have collected the information in tables, so if you need to know how strong a bond is, you can just look up the information you need. Bond strengths are not always easy to predict, because the strength of a bond depends on a number of factors.
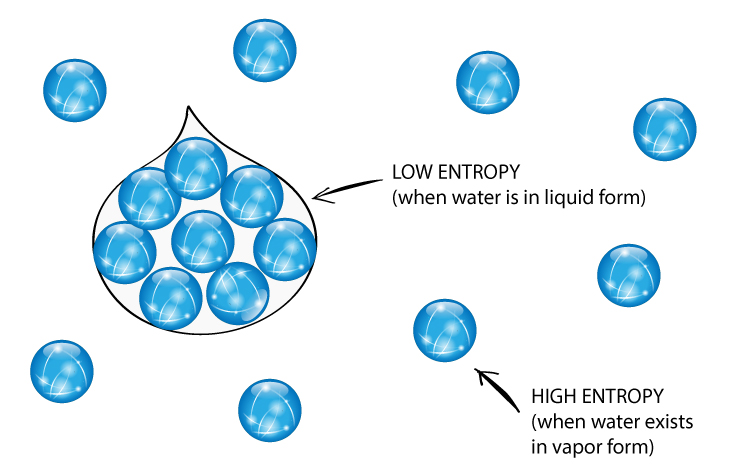
A reaction is endothermic if bond-breaking costs more energy than what is provided in bond-making.īond energies (the amount of energy that must be added in order to break a bond) are an important factor in determining whether a reaction will occur.the entropy of a pure substance at 298 K and 1 atm pressure). Standard molar entropies are listed for a reference temperature (like 298 K) and 1 atm pressure (i.e. A reaction is exothermic if weaker bonds are traded for stronger ones. The entropy of a substance has an absolute value of 0 entropy at 0 K.A reaction is exothermic if more energy is released by formation of new bonds than is consumed by breaking old bonds.

Whether a reaction is able to go forward may depend on the balance between these bond-making and bond-breaking steps. It costs energy to break bonds, but energy is released when new bonds are made. Some of the bonds in the reactants are broken, and new bonds are made to form the products. In a reaction, there is a change in chemical bonding. Why does the energy of a set of molecules change when a reaction occurs? To answer that, we need to think about what happens in a chemical reaction. non entropy concept for various uses in theoretical organic chemistry and che. It has less energy left over if it gave some away. Shannon entropy analysis was also applied in quantum mechanics.
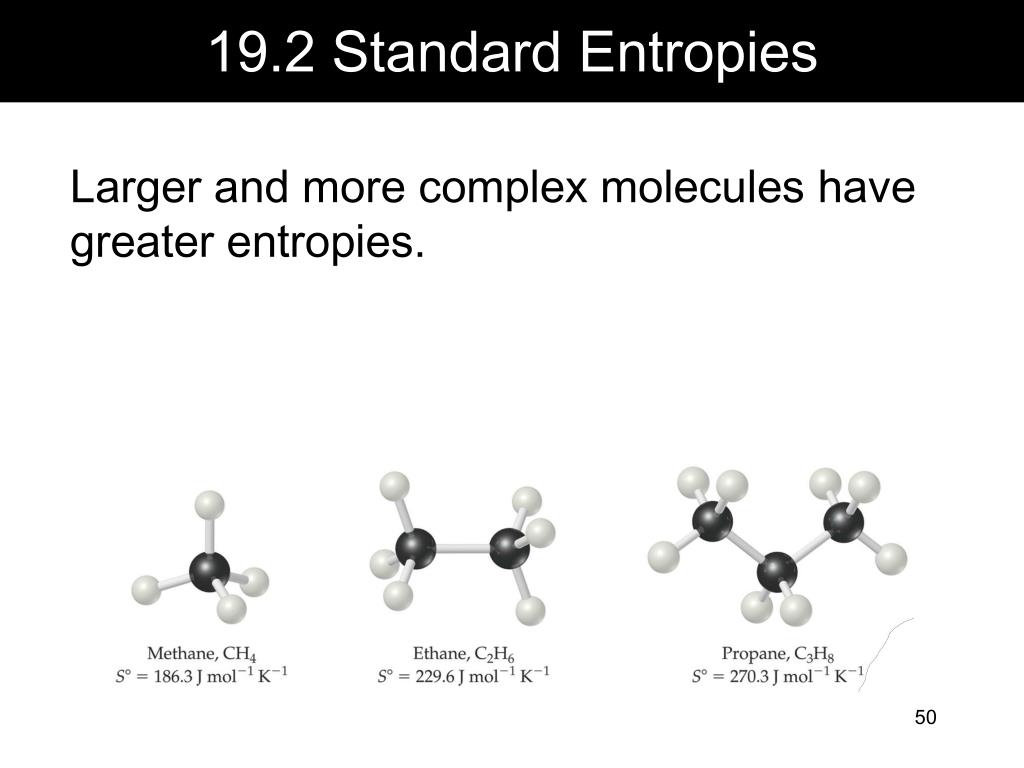
A positive value indicates an increase in entropy, while a negative value denotes a decrease in the entropy of a system. Usual units of standard molar entropy are joules per mole Kelvin (J/mol·K). If a system undergoes a reaction and gives off energy, its own energy content decreases. Standard molar entropy is defined as the entropy or degree of randomness of one mole of a sample under standard state conditions. That last statement is a lot like the description of energetics on the previous page. A reaction is favored if the enthalpy of the system decreases over the reaction.The enthalpy change of a reaction is roughly equivalent to the amount of energy lost or gained during the reaction.Enthalpy is the heat content of a system.We will see in the next section that there is another energetic factor, entropy, that we also need to consider in reactions. Roughly speaking, the energy changes that we looked at in the introduction to thermodynamics were changes in enthalpy. Similarly, the energy of the molecules that do not take part in the reaction is called the "external enthalpy" or the "enthalpy of the surroundings". Sometimes, we call it the "enthalpy of the system." These two phrases refer to the same thing. Sometimes, we call the energy of the molecules undergoing change the "internal enthalpy". High-entropy materials (HEMs) have attracted great attention due to the distinctive designing concept and unique properties which are expected to make new advances in several energy conversion and storage technologies. when energy is added) or decreases (because energy is given off) is a crucial factor that determines whether a reaction can happen. Whether the enthalpy of the system increases (i.e. The heat that passes into or out of the system during a reaction is the enthalpy change. Enthalpy is a central factor in thermodynamics. Thermodynamics is the study of the relationship between heat (or energy) and work.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
